[LMD publishes] Parameterization of wind-driven snow transport in Antarctica
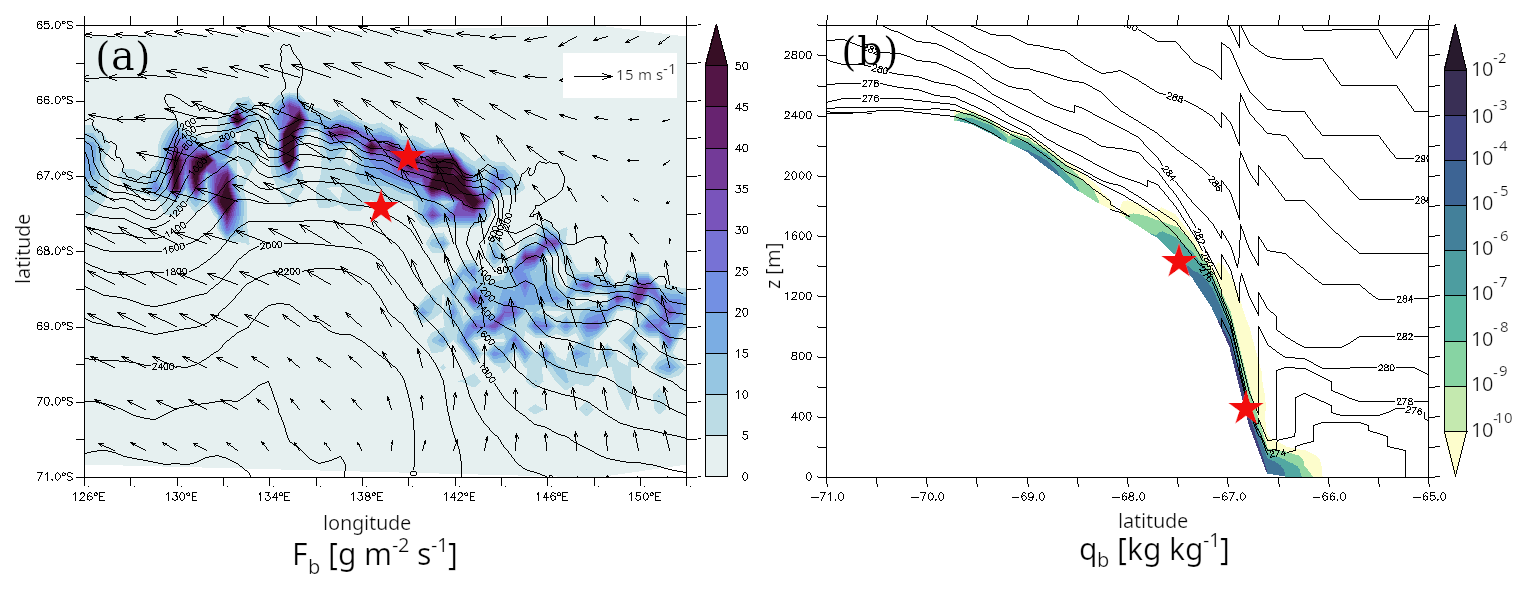
Wind-driven snow transport, known as blowing snow, plays a major role in the redistribution of snow in Antarctica and influences the surface mass balance of the ice sheet. In order to better represent this process in global climate models, a new intermediate-complexity parameterization has been developed and implemented in the LMD global atmospheric model ICOLMDZ.
This parameterization represents snow erosion, transport, and deposition by the wind. It has been evaluated using simulations over Antarctica and comparisons with observations from automatic weather stations. The results show that the model realistically reproduces the timing of blowing-snow events, while providing simulated fluxes of consistent orders of magnitude.
This work contributes to improving the reliability of climate simulations in polar regions, particularly for studies of the Antarctic surface mass balance.
- Contact : Étienne Vignon (etienne.vignon@lmd.ipsl.fr)
- Link : Vignon, É., Chiabrando, N., Agosta, C., Amory, C., Wiener, V., Charrel, J., Dubos, T., and Genthon, C.: Intermediate-complexity parameterisation of blowing snow in the ICOLMDZ AGCM: development and first applications in Antarctica, Geosci. Model Dev., 19, 239–259, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-19-239-2026, 2026.

