[LMD publishes] The first observations of the atmospheric CO2 isotope ratio δ13C by Lidar
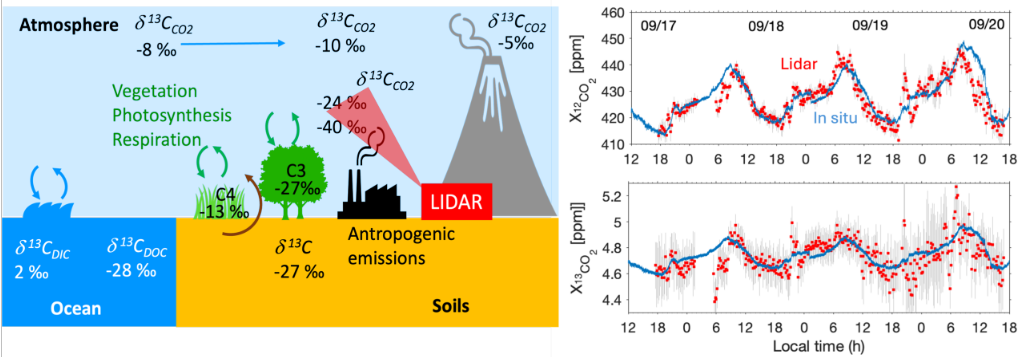
Measuring the ratio of the stable isotope δ13C to CO2 in the atmosphere has the potential to characterize: (1) the biogeochemical processes of surface-atmosphere exchange (photosynthesis, respiration), (2) the sources of CO2 (organic decomposition, anthropogenic emissions), and (3) ecosystems (C3 and C4 plants), and to monitor their distribution and evolution in the context of climate change. Within this framework, the LMD (Laboratory of Microbiology and Biotechnology) conducted a first measurement of δ13C using ground-based Lidar with the COWI (CO2 & Wind Lidar) instrument. This pioneering work allows us to assess the feasibility of airborne and space-based measurements to provide information on the “process” or “origin” of the measured CO2 concentration.
Contact : Fabien Gibert, gibert@lmd.polytechnique.fr
Link : Gibert, F., Edouart, D., Mondelain, D., Cénac, C., and Yver, C.: δ13C carbon isotopic composition of CO2 in the atmosphere by Lidar. A preliminary study with a CDIAL system at 2-µm, Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, EGUsphere [preprint], https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-2025-1039, 2025

